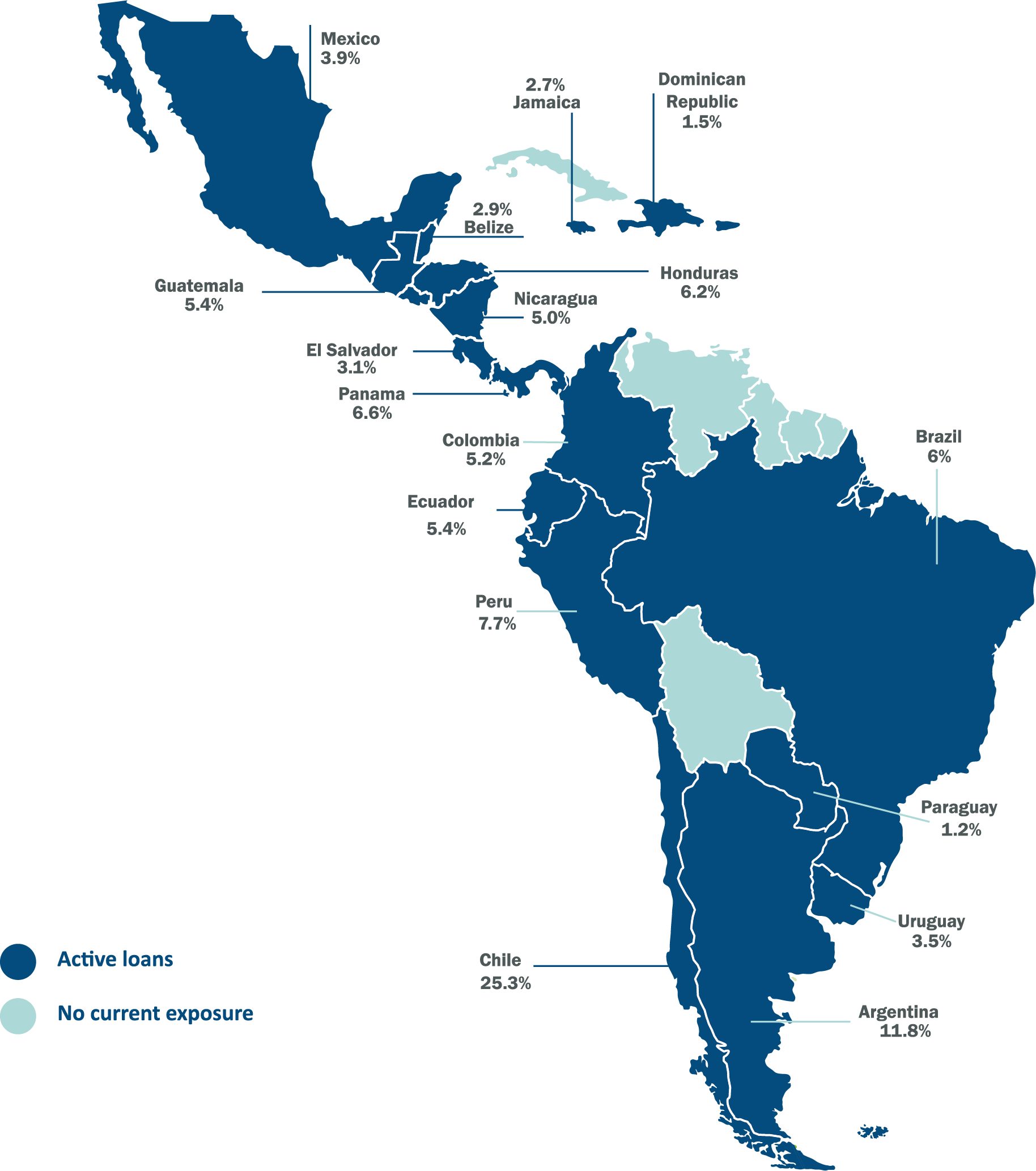
CIFI is a leading private sector middle-market infrastructure platform in Latin America and the Caribbean.
Our platform serves the entire Latin American and Caribbean Region with sustainable investments that target positive impact and integrate environmental, social, and corporate governance factor.
Infrastructure is a key driver for Latin America and the Caribbean region for post-COVID-19 recovery. Regional governments depend largely on private sector investment to support growth. IDB estimates an infrastructure investment gap in the region around 2.5% of GDP, posing a rich opportunity for private sector investments.
Project finance has been a key driver of infrastructure development boosting economies in Latin America during the past decade and will continue to do so in the next decade as the range of investors diversifies, grows, and increases in sophistication.
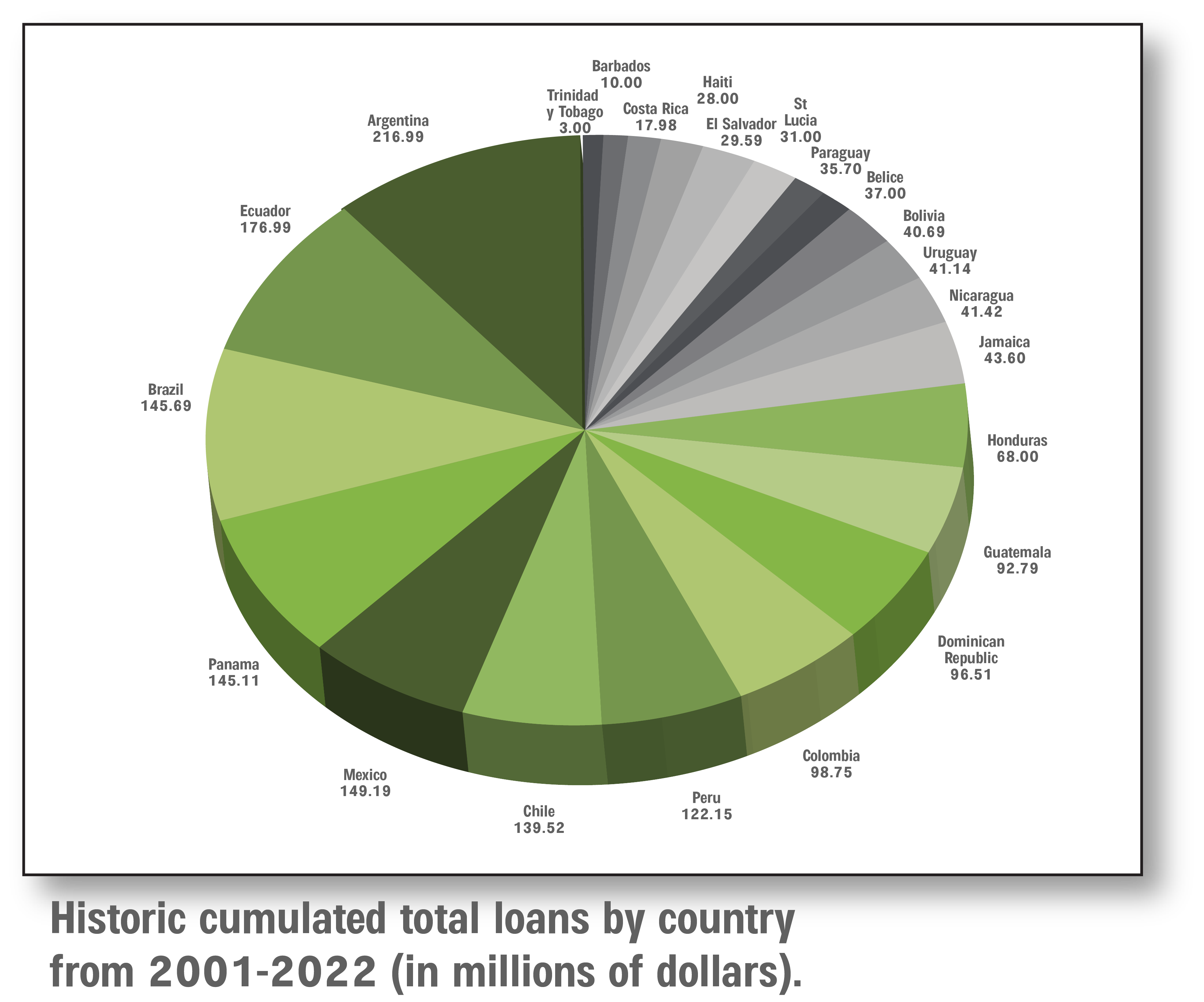
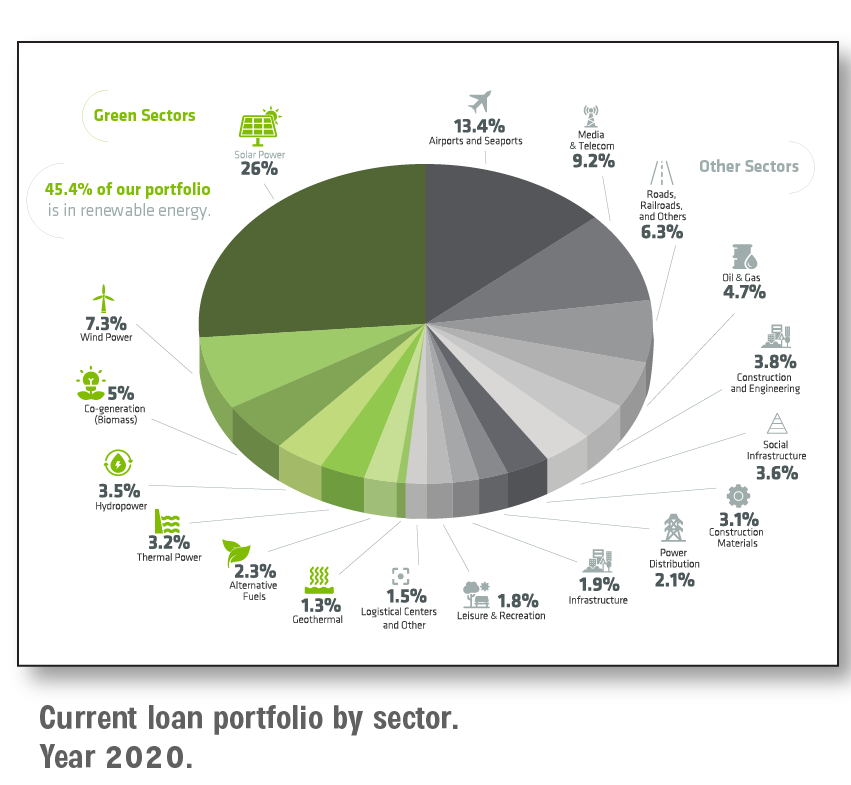
CIFI, with a track record of 20 years in the region, has financed over 200 projects, with US$1.8 billion in direct lending and more than US$20 billion in mobilized capital.







Social Infrastructure
Defined as critical infrastructure that support human wellbeing, Social Infrastructure is at the center of the Sustainable Development Agenda.
In Latin America, the Covid-19 crisis brought to light the urgent need to increase investment in social infrastructure, especially in health care, education, water, and sanitation. Participation from the private sector will accelerate the growth that in turn will boost economic development by reclaiming the millions of jobs lost during the pandemic.
Social infrastructure is the construction and maintenance of facilities that support social services. Types of social infrastructure include healthcare (hospitals), education (schools and universities), public facilities, smart cities, water and sanitation, and waste management facilities.